In Kenya, Open Contracting Improves Efficiency & Curbs Corruption
On 31st August 2020, President Uhuru Kenyatta directed the Ministry of Health to come up with a transparent, open method and mechanism through which all tenders and procurement done by Kenya Medical Supplies Agency (KEMSA) will be available online. The directive follows allegations of corruption in the procurement of COVID-19 emergency supplies.
With citizens’ lives on the line and government spending at record highs, ensuring accountability to citizens is imperative to maintaining trust and effectively managing KEMSA’s procurement in response to COVID-19. Open procurement data can help in improving the efficiency of emergency procurement and support civil society groups to detect corruption and monitor the effectiveness of service delivery.
“This level of transparency and through the use of technology will go a very long way in ensuring that we have the confidence of our people that those placed in institutions are able to manage the resources of the Kenyan taxpayer plus our development partners in an open and transparent manner” – President Uhuru Kenyatta
Much can be learned from Makueni County in Kenya, a county that publishes and uses open, accessible, and timely information on government contracting to engage citizens and businesses. The Makueni Open Contracting Portal is an interactive site built by Development Gateway (DG) that provides detailed information on each step of the tender, award, and contract implementation process at the county level. These steps are now recorded within the interactive Makueni Open Contracting Portal – making information available for citizens at each step of the process. The county plans to go a step further to publish all implementation data such as community monitoring reports, also known as PMC reports and supplier payment vouchers.
The goal of the portal is to improve the efficiency of public procurement management and support the delivery of higher-quality goods, works, and services for residents of Makueni County through enhanced citizen feedback.
What We Learned from Makueni County
Lesson 1: Public Data Improves Efficiency
The primary role of the Ministry of Health and KEMSA in Kenya during an emergency situation is to provide citizens timely, affordable, and efficient supplies and services. Digitizing and publishing procurement data will provide the Ministry insights on whether funding and services are reaching intended beneficiaries.
Publishing procurement data will also encourage better monitoring from relevant state and non-state actors. The Ministry of Health and KEMSA will have the opportunity to aggregate non-state actors’ feedback and state actor insights. This feedback will enable them to make data-driven decisions that will improve service delivery to citizens, promote efficient allocation of resources and ultimately saving costs.
DG has developed interactive M&E dashboards to support analysis currently used by Makueni County. The series of charts and visualizations provide helpful data insights – such as top suppliers that received contracts and the percentage of awards that go toward the Access to Government Procurement Opportunities (AGPO), which requires tenders to be awarded to women, youth, and people with disabilities.
Since the start of the use of the Makueni open contracting portal in 2019, improved resource utilization and efficiency in procurement has been identified by the County leadership. Governor Kivutha Kibwana cited that the County has saved Kes. 30,000,000 from the Roads department as a result of using the portal.
Lesson 2: Building Trust is Essential to Combating Corruption
The complexity of emergency responses such as COVID-19 requires cooperation between the private sector, national, and county government to ensure timely delivery of supplies. KEMSA publishing data will promote feedback and engagement of business and citizens further building trust and collaboration. Publishing procurement data also equips civil society and citizens with the information needed to help combat corruption. For example, reporting counterfeits, frauds, and scams – which has been a key corruption issue identified globally in COVID-19 response procurement, particularly PPEs.
DG has implemented its corruption risk dashboard in Makueni, which uses high powered analytics and global research to identify risk profiles for potential corruption in procurement. KEMSA can adopt the corruption risk dashboard as a red-flagging tool to assist in identifying procurement activities that merit in-depth auditing of corruption risk – including fraud, collusion, and process rigging – over time. These analytics will allow the organization to address cases of corruption before taxpayer money is lost.
Lastly, publishing Beneficial ownership data can enable governments to quickly perform minimal standards of due diligence on companies they are buying goods and services from. As well as reducing the immediate risk of corruption, beneficial ownership data provides a valuable trail for future audit.
Related Posts

Introducing The HackCorruption Civic Tech Tools Repository
Introducing the Civic Tech Tools Repository: an open-source hub of digital solutions to fight corruption. Designed for growth through GitHub contributions, it brings together tools, code, and resources across six key areas for HackCorruption teams and beyond.

From Standardization to Specificity: Localizing Multi-Country Research
Multi-country research must balance consistency with local realities. While standardization allows reliable comparisons and generalizable insights, local context shapes outcomes. This blog explores how programs can strike that balance effectively.

Economic Toll of Tobacco-Related Diseases in Kenya: New Research Findings
Development Gateway: An IREX Venture (DG) is pleased to announce the publication of a research manuscript on the Economic Costs of Tobacco-Related Illnesses in Kenya. This research was carried out as part of the Tobacco Control Data Initiative (TCDI) activities in Kenya and is part of a broader report on Morbidity and Mortality from Tobacco Use in Kenya.
Development Gateway: An IREX Venture (DG) is pleased to announce the publication of a research manuscript on the Economic Costs of Tobacco-Related Illnesses in Kenya. This research was carried out as part of the Tobacco Control Data Initiative (TCDI) activities in Kenya and is part of a broader report on Morbidity and Mortality from Tobacco Use in Kenya. Data from this research is available on the TCDI Kenya dashboard, which aims to supply decision-makers in government, members of civil society, and academia with improved access to country-specific data to better inform tobacco control policy.
Published in August 2024 in the Tobacco Use Insights journal, this is the third of three manuscripts that seek to break down the research report’s findings. The first, published in November 2023, explored the prevalence, patterns, and factors associated with tobacco use among patients with tobacco-related illnesses (TRIs), such as cancers, cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease, and diabetes. The second, published in July 2024, focused on Mortality from Tobacco Use in Kenya. You can access its accompanying blog post here.
This blog highlights some key findings in the manuscript, based on the research carried out in Kenya from 2021-2022, estimating the direct, indirect, and ultimately economic costs of tobacco use for the period studied.

Why research on the economic burden of tobacco use in Kenya?
Indirect and direct medical costs of treating TRIs can place a significant economic burden on societies through healthcare and productivity losses. This is especially true for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), which bear the brunt of the global tobacco crisis, accounting for a staggering 80% of tobacco-related deaths worldwide. As a result, assessing the economic impact of tobacco consumption in LMICs is crucial for shaping effective tobacco regulation and policy. However, this has been understudied in Africa, and the data that is available remains scant. In Kenya, estimating the economic costs of tobacco use is imperative to making informed, evidence-based policy decisions.
This manuscript not only reveals the direct financial burden of tobacco use but also offers a solid foundation for defining the necessary policy actions to address its harmful health and economic consequences. Additionally, it highlights the far-reaching effects of exposure to secondhand smoke for non-smokers, responsible for an estimated 1.3 million deaths annually worldwide. Barring effective tobacco control interventions, LMICs will be up against higher tobacco-related healthcare costs, placing even more strain on already overwhelmed healthcare systems.
Key Findings from the Research
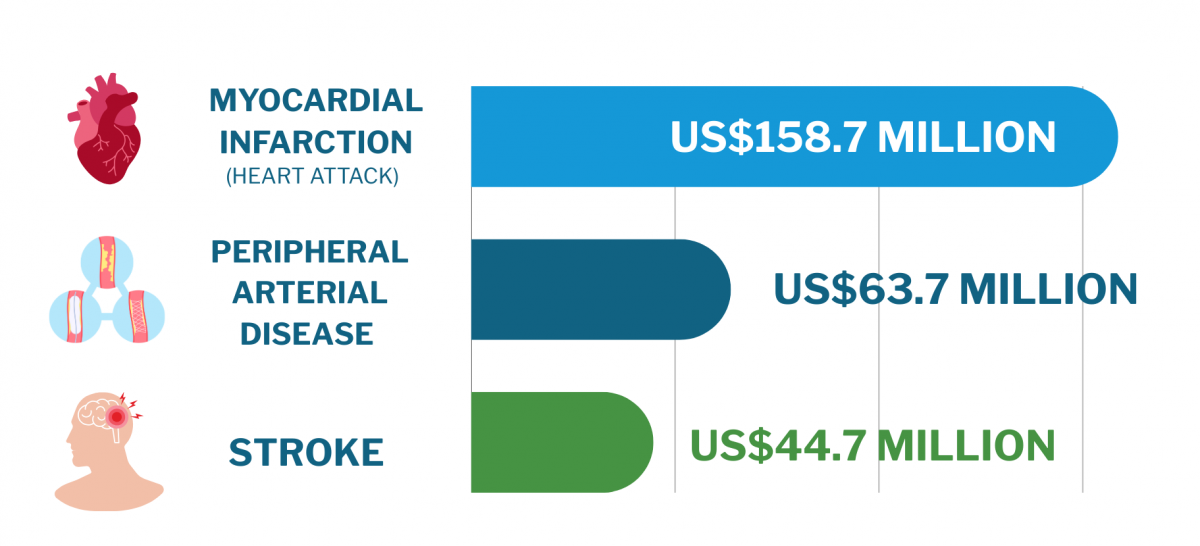
The estimated healthcare costs linked to tobacco use in Kenya are an alarming US$396.1 million (approximately 53.4 billion KES). Among the tobacco-related illnesses (TRIs) studied, myocardial infarction (heart attack) was the leading cost driver, accounting for US$158.7 million (approximately 21.42 billion KES). Following that, peripheral arterial disease and stroke each contributed US$63.7 million (approximately 8.74 billion KES) and US$44.7 million (approximately 6.02 billion KES) in healthcare expenses, respectively. A significant portion of these costs -over 90% – is driven by the expense of medications required to manage these conditions.
Regarding productivity losses due to tobacco-related illnesses, the costs range from US$148 (approximately 19,980 KES) per person to US$360 per person (approximately 48,600 KES), making up between 27% and 48% of the total economic burden. Productivity losses from the diseases ranged between US$148 (approximately KES 19,980) and US$360 (approximately KES 48,600), accounting for 27% to 48% of the economic costs.
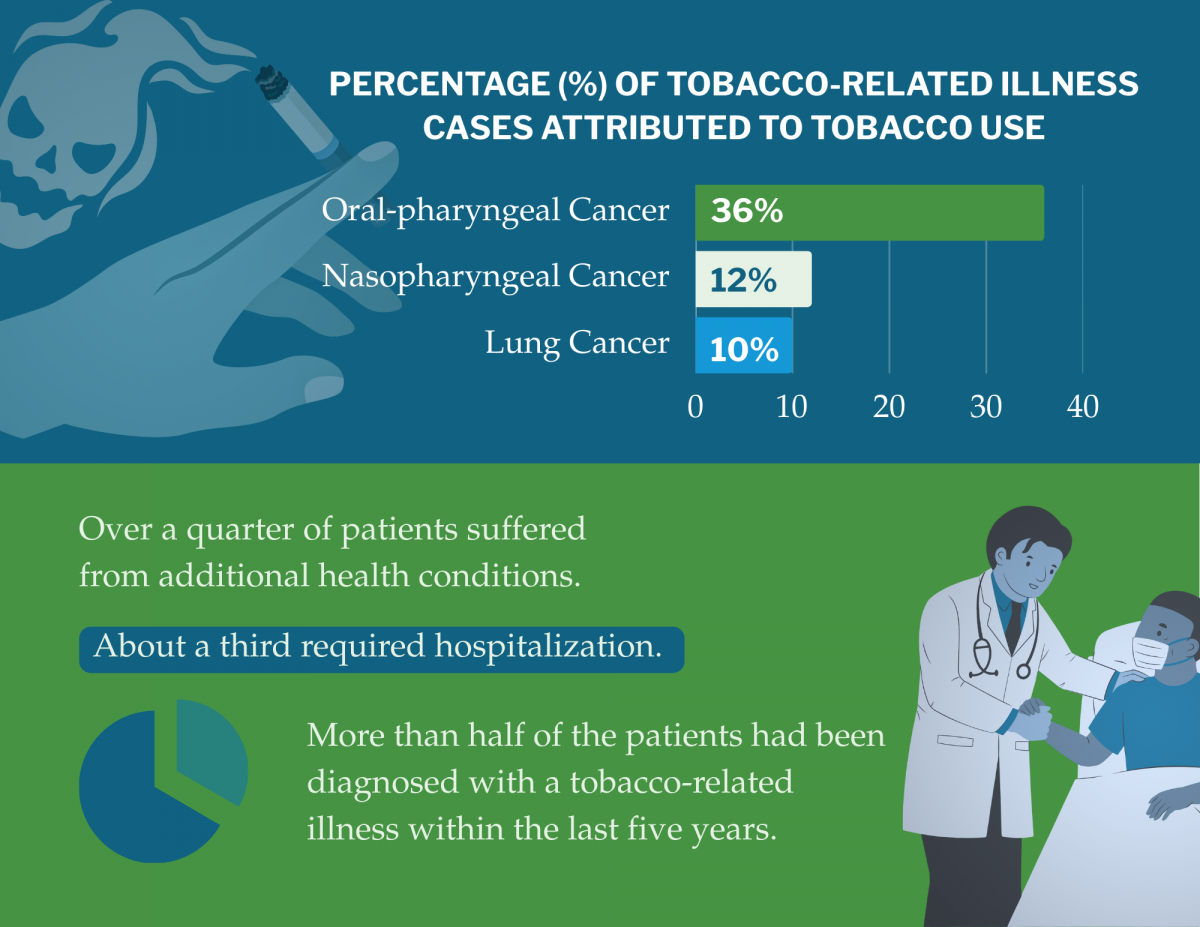
In terms of healthcare costs per case, lung cancer was the most expensive, costing US$23,365 (approximately KES 3,150,275) per case, followed by oral-pharyngeal cancer at US$7,637 (approximately KES 1,031,995), and laryngeal cancer at US$6,922 (approximately KES 933,470).
In 2022, the tobacco industry in Kenya generated $7.35 million in revenue, representing 7% of the country’s GDP of US$105 billion. However, the economic cost of tobacco use – just for the illnesses included in the study – accounts for more than 34% of this revenue. In other words, the financial toll of tobacco use in Kenya ranges from US$544.74 million (approximately KES 73.5 billion) to US$756.22 million (approximately KES 102.1 billion), while the tobacco industry’s contribution to the country’s GDP is much smaller at US$252.93 million (approximately KES 34.1 billion).
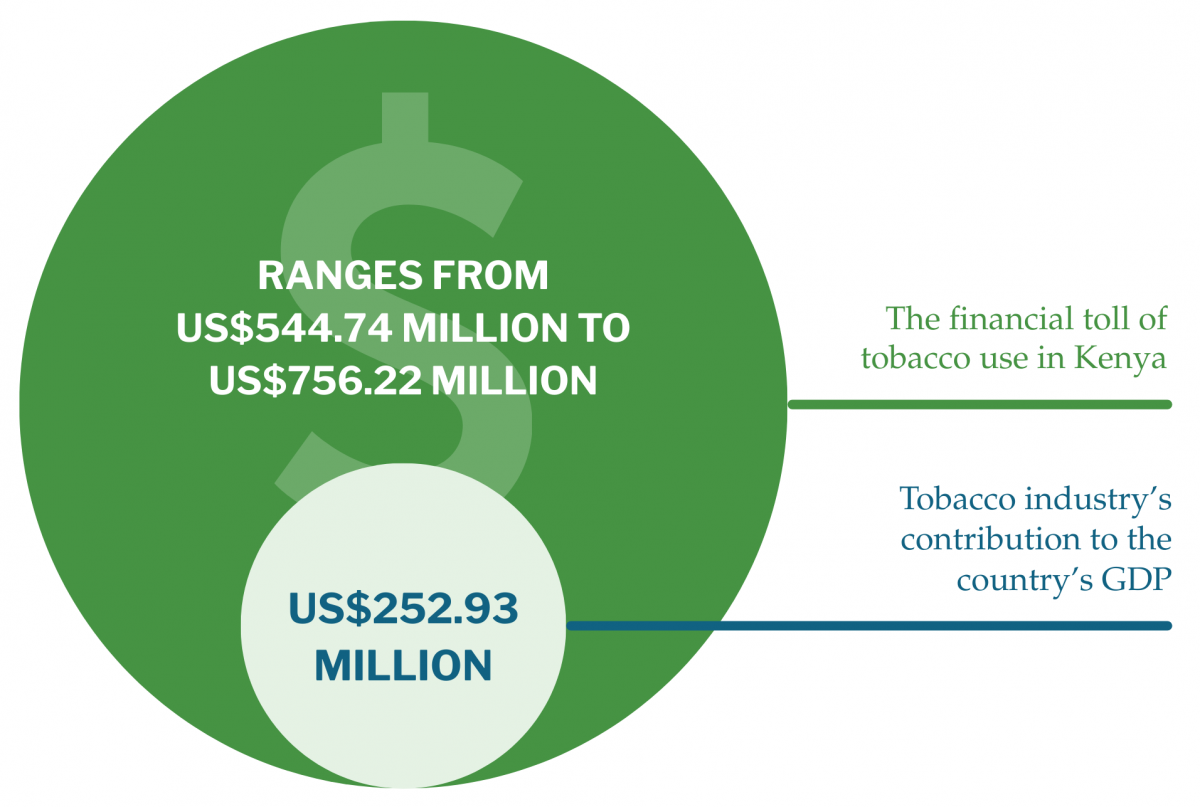
When comparing these figures, tobacco use results in a net loss to the economy of between US$291.8 million (approximately KES 39.4 billion) and US$503.3 million (approximately KES 67.9 billion) each year. This means that for every dollar the tobacco industry earns, the economy loses between KES 297 and KES 405 in healthcare costs and lost productivity, illustrating a poor return on investment.
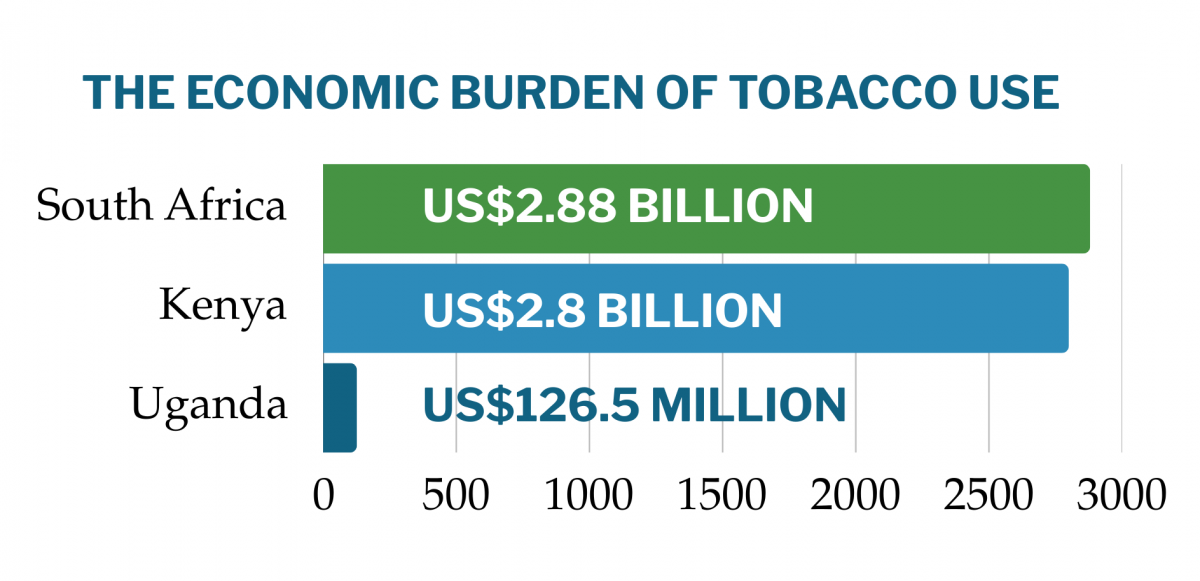
The analysis further shows that treating tobacco-related illnesses (TRIs) in Kenya is an enormous financial burden on the healthcare system, with total treatment costs estimated at US$2.8 billion (approximately KES 378 billion). Of this, US$396.1 million (approximately KES 53.4 billion) is attributed explicitly to tobacco use, accounting for 14% of the overall costs of managing these diseases. In terms of comparison, the economic burden of tobacco use in Kenya is somewhat less than in South Africa, where the cost is US$2.88 billion (approximately KES 388.8 billion), but more than in Uganda, where the cost is US$126.5 million (approximately KES 17.1 billion).
These differences can be attributed to varying smoking rates and the prevalence of tobacco-related illnesses in each country.
Implications for Policy
To address the economic and health impacts of tobacco use in Kenya, several key policy recommendations can be made:
- Strengthen Tobacco Control Laws: Implement comprehensive tobacco control legislation, enforce existing laws rigorously, and increase taxes on tobacco products to make them less affordable and accessible.
- Promote Cessation Programs: Advocate for the introduction of more support services for people trying to quit smoking, as well as monitor the tobacco industry’s activities to ensure they comply with existing regulations.
- Engage Stakeholders and Raise Awareness: Build stronger collaborations with relevant stakeholders, run public awareness campaigns to educate people about the dangers of tobacco use, and encourage policymakers to prioritize tobacco control on the national agenda.
- Capacity Building for Enforcement: Invest in strengthening enforcement mechanisms and provide training for healthcare professionals on effective tobacco cessation strategies.
- Leverage International Partnerships: Work with international organizations to tap into their expertise and resources, ensuring the successful implementation of tobacco control measures.
- Adopt Global Best Practices: Align local policies with global best practices and evidence-based strategies to enhance tobacco control efforts in Kenya.
- Use Research to Inform Policy: Use ongoing research and data to develop evidence-based policies supporting tobacco cessation and reducing tobacco-related harm.
By adopting these policy measures, Kenya can mitigate the significant economic burden of tobacco use and work towards better health outcomes for its population.
If you would like to learn more about TCDI and explore country-specific data, kindly visit www.tobaccocontroldata.org.
