GDPR and its Connection to the Open Data Movement
Since this past May, you’ve probably received a flood of company emails updating terms of service and consent requests to give permission to collect your data. You also probably know that this flood is all thanks to the EU’s recent General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which has set us abuzz in its heightened protection of EU citizen data. But as members of the open data community, what does GDPR mean for our global movement? How can GDPR influence our clients, partners, and broader data-driven work?
What Kind of Data Are We Talking About?
GDPR covers two data types: biometric, data containing information that could be used to specifically identify a person; and personal, data that, when matched with other identifiers, could directly or indirectly identify a person. In practice, these two data types extend from a person’s IP address, to his or her political opinions, geographic location and shopping habits.
In evaluating data and its significance (should it be protected – and if so, how?), context is paramount. Plenty of data collected doesn’t reveal identity (e.g. visiting a website), but what happens when multiple data points are combined (e.g. tracking website visitors’ IP addresses and download patterns), producing results that bring up privacy questions?
How are GDPR and Open Data Connected?
GDPR isn’t the only policy taking a closer look at protecting data – a number of organizations in the development space have rigorous data access and privacy policies. Both the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the UK’s Department for International Development have open access policies requiring all research they fund to be available publicly, along with raw datasets upon request during and after project conclusion.
USAID has an internal policy protecting the data of its employees and partners, as well as a Data Security Guidance resource for USAID implementing partners, outlining procedures for safeguarding beneficiaries and best practices in collecting, storing, and discarding project data. UNICEF has worked for several years to protect children’s information on- and offline, recently providing guidance to the ICT sector on creating policies to better protect children’s data.
As a data-driven organization taking a holistic approach to data collection and use, DG has tackled data privacy by prioritizing open source tools and building our flagship Aid Management Platform and geocoding tool to allow any user to use and edit our software freely. In Sudan, we worked with DFID on how to balance the aim of releasing data on humanitarian activities with the ongoing need to obtain consent in the release of sensitive information.
We’ve used ‘location fuzzing’ in Ghana to protect hospital and health service locations, and in building the resource portal for Plan International’s Missing Child Alert to protect service locations of trafficking victims. And to balance different access policies for the UNDG Information Management System, we built the API with some public pages, and others requiring a login to protect departments’ sensitive data.
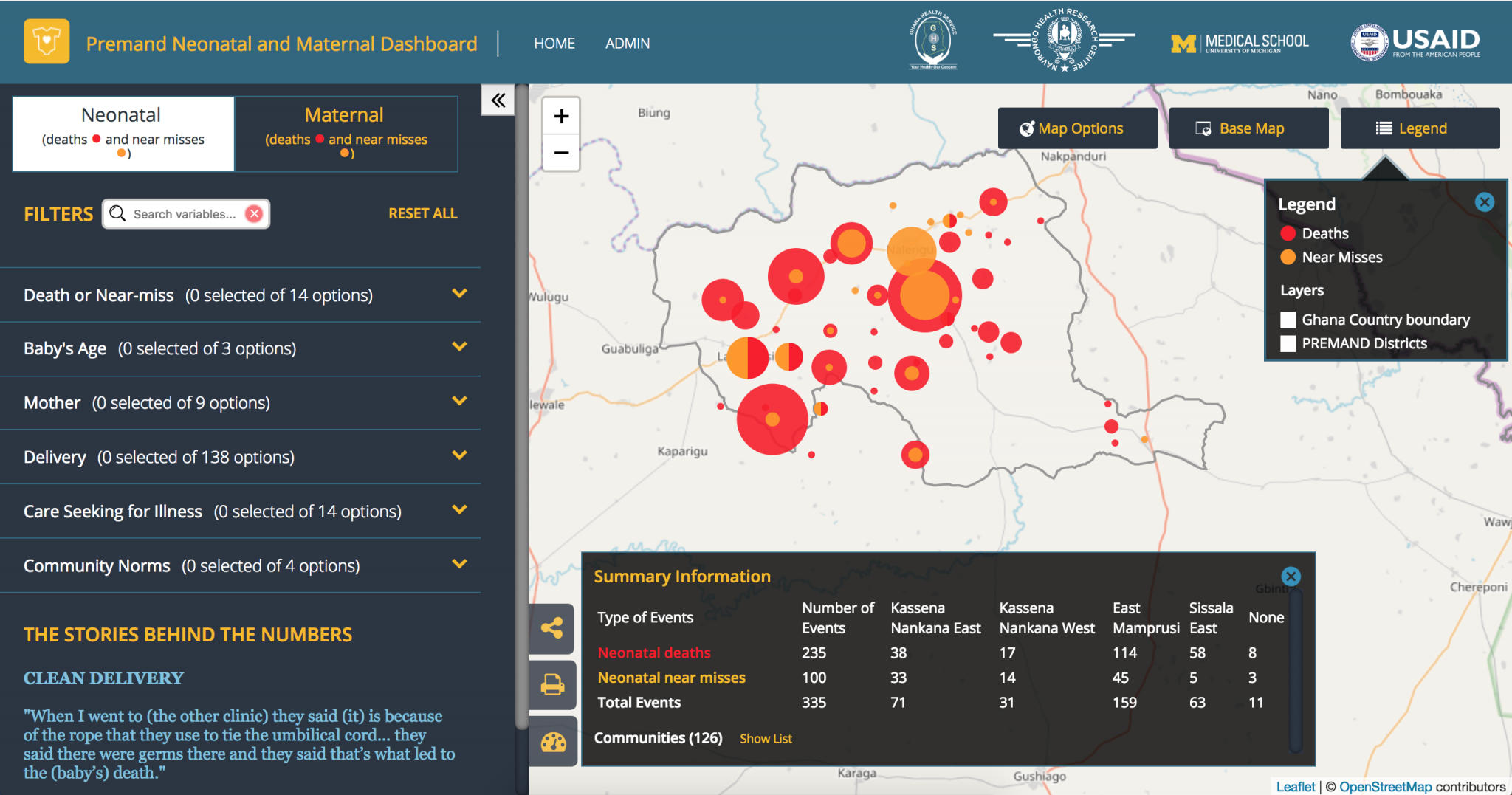
Figure 1: The PREMAND project‘s Mapping Portal, which uses “location fuzzing” to protect health and location data of individuals.
Through our work, we’ve learned that there’s room for improvement within our community – particularly in how we keep records of explicit consent and in how we plan for data breaches. When data privacy isn’t taken seriously, it can put lives, progress, and initiatives at risk.
What Can We Do Practically to Protect Data?
When thinking about how to assess our own programs or advise partners on how to step up data privacy controls, five simple steps can be taken to improve data protection:
- Take Stock: Determine what personal information is collected and kept in your files;
- Scale Down: Maintain only data that is absolutely necessary;
- Throw it Out: If you don’t need it, (safely) get rid of it;
- Secure it: Keep data safe;
- Plan Ahead: Create a plan to respond to data breaches.
Taking stock is about understanding context – what data is collected, why, by whom, and for how long. With a broad understanding of how you collect data and what it’s used for, you can then determine what a reasonable limit should be in collecting and storing your data.
Scaling down is about only keeping strictly necessary data. If you do this, the next steps happen naturally – safely discard unnecessary data, and ensure that what remains is secure. “Secure” can mean any combination of controls, from anonymizing data, to protecting individual identity, to installing passwords, firewalls, and “read only” features.
Lastly, in the event of a data breach, you need an established plan detailing what to do, who to notify (e.g. individuals whose data has been compromised), and any immediate steps to mitigate risks (e.g. temporary blocking access to online files).
In Sum
The open data world in particular has long been familiar with issues of data protection and access. Due to this familiarity, data and digital development partners are ideally positioned to encourage & build best practices – it’s time for us to proactively take up this responsibility. GDPR is simply a reminder for us that open data is a balancing act: we must prioritize both the protection of individual data and increase access to vital information.
Share This Post
Related from our library

Introducing The HackCorruption Civic Tech Tools Repository
Introducing the Civic Tech Tools Repository: an open-source hub of digital solutions to fight corruption. Designed for growth through GitHub contributions, it brings together tools, code, and resources across six key areas for HackCorruption teams and beyond.

Building a Sustainable Cashew Sector in West Africa Through Data and Collaboration
Cashew-IN project came to an end in August 2024 after four years of working with government agencies, producers, traders, processors, and development partners in the five implementing countries to co-create an online tool aimed to inform, support, promote, and strengthen Africa’s cashew industry. This blog outlines some of the key project highlights, including some of the challenges we faced, lessons learned, success stories, and identified opportunities for a more competitive cashew sector in West Africa.

Digital Transformation for Public Value: Development Gateway’s Insights from Agriculture & Open Contracting
In today’s fast-evolving world, governments and public organizations are under more pressure than ever before to deliver efficient, transparent services that align with public expectations. In this blog, we delve into the key concepts behind digital transformation and how it can enhance public value by promoting transparency, informing policy, and supporting evidence-based decision-making.