Keeping CALM to Design a National M&E System for Malawi
The Government of Malawi’s National Agriculture Investment Plan and existing M&E framework outlines priority areas for measuring results – however, currently there is no system for measuring progress against these goals. Without the ability to measure progress, how can we evaluate policy effectiveness?
In Malawi, the government has recognized that an M&E management information system can improve the use of data and evidence to support decision-making at sub district, district, and central levels. Since 2017, DG has collaborated with the Malawi Ministry of Agriculture, Irrigation, and Water Development (MoAIWD) in country level data use support, as part of Phase II of the the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation-supported Results Data Initiative. Our aim was to support the design of a framework for a National Agriculture Management Information System (NAMIS).
Today, DG is pleased to announce the publication of the Conceptual Framework for the Design of the National Agriculture Management Information System (NAMIS) and its accompanying Executive Summary. The reports inform sustainable and effective design of the NAMIS, and provide actionable recommendations for MoAIWD as it moves through implementation.


Figure 1: Conceptual Framework for the NAMIS Full Report; Figure 2: NAMIS Executive Summary
To ensure NAMIS responds to the needs of MoAIWD and the wider agriculture sector, its design centers around potential users. DG and MoAIWD conducted a landscape analysis – of priority decisions, data and tools, and barriers to more effective data use across the agriculture sector. We asked 75 future users from national to local levels – in government, private sector, NGOs, and development partner organizations – what decisions they wanted NAMIS to help them make.
The Custom Assessment and Landscaping Methodology (CALM) methodology informed our analysis, to ensure a system design that truly supports successful organizational strategy and adaptation.
Because the system has various intended users, multiple data sources, and different levels of system use, NAMIS will be built using a modular structure – so that users can easily access the data most relevant to their work. The system will be divided into 15 modules, and we recommend a three phase implementation. Each phase will focus on different “module types.” Together, phased implementation and a modular structure help ensure NAMIS is an efficient M&E system that addresses the needs of all sector stakeholders.
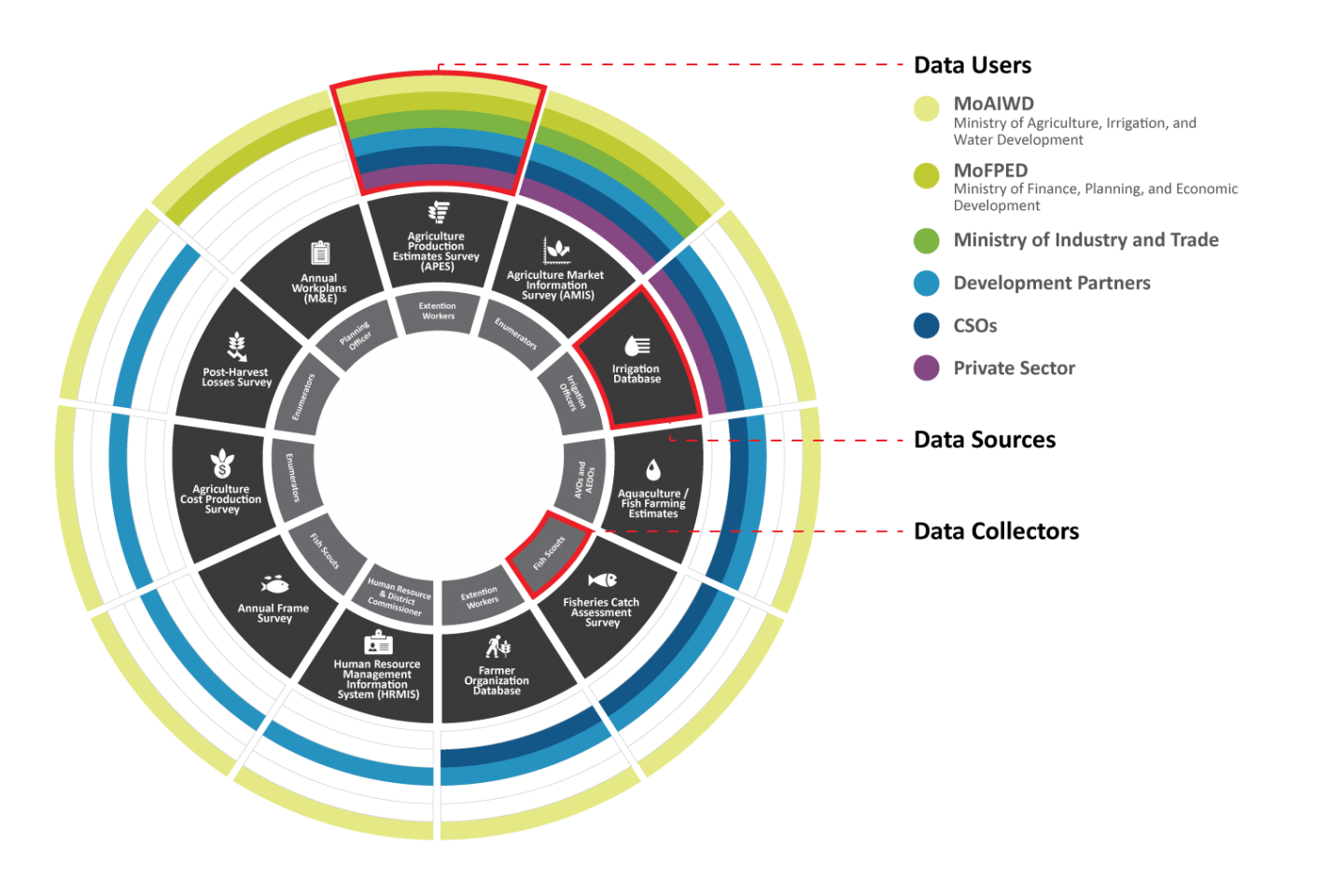
Additionally, two practical assessment outputs are user journeys and a data ecosystem map. User journeys outline how future NAMIS users interact with data to make key decisions, which users make specific decisions, and which data sources are most useful for decision-making. The data ecosystem map provides a comprehensive picture of the Malawi agriculture sector, highlighting which data are currently gathered and used by which actors.
Figure 3: Malawi Agriculture Data Ecosystem Map
We look forward to collaborate with MoAIWD as they are currently using the Conceptual Framework to implement the first phase of the NAMIS using DHIS2. With this clear framework to build on, we hope to set up MoAIWD for a deep contextual understanding, smooth NAMIS implementation, and sustainable data use policies and processes.
Beyond the launch of the Conceptual Framework, we look forward to continuing to use our M&E framework to establish needs-based country systems. We’ve already begun to share learnings and insights from building the Framework at the Complexity and Policy Studies (CAPS) Conference in Washington, D.C. this spring, to inform system design in a wider policy context.
Stay tuned for more updates on the blog as we continue to implement NAMIS modules and “stay CALM” to build user-centered systems.
Share This Post
Related from our library

Development Gateway Collaborates with 50×2030 Initiative on Data Use in Agriculture
Development Gateway announces the launch of the Data Interoperability and Governance program to collaborate with the 50x2030 initiative on data use in agriculture in Senegal for evidence-based policymaking.

Reflecting on 3 Years of Digital Advisory Support for Agricultural Transformation
As the DAS program concludes, this blog reflects on its impact in advancing digital transformation in agriculture, highlighting lessons on capacity building, knowledge transfer, and sustaining resilient food systems.

From Standardization to Specificity: Localizing Multi-Country Research
Multi-country research must balance consistency with local realities. While standardization allows reliable comparisons and generalizable insights, local context shapes outcomes. This blog explores how programs can strike that balance effectively.