
New Research Reveals Reasons for Shisha Smoking in Nigeria
Today, we’re excited to announce our Tobacco Control Data Initiative (TCDI) published groundbreaking research shedding light on reasons for shisha smoking across Nigeria. The research paper, “Reasons for shisha smoking: findings from a mixed methods study among adult shisha smokers in Nigeria,” was published by PLOS Global Public Health and provides vital context-specific evidence to inform the national response to increased shisha smoking. This study, the first of its kind to be conducted in Nigeria, used a mixed methods approach and covered all geographical regions of Nigeria. It was produced in partnership with R-DATS consulting and funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Key Findings
The research, led by Dr. Noreen Dadirai Mdege, comprises in-depth interviews with 78 current shisha users in 13 states, along with a quantitative survey involving 611 current shisha users across 12 states, spanning Nigeria’s six geopolitical zones.
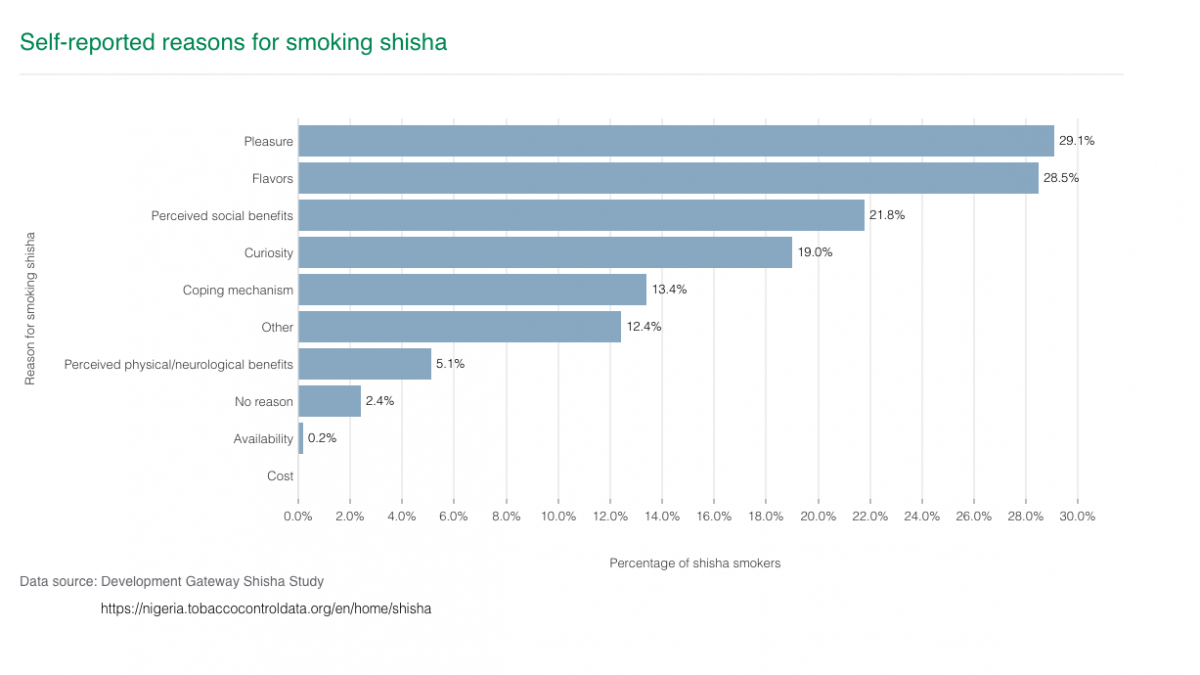
One of the most common, self-reported reasons for smoking shisha was shisha flavors. Shisha came in a variety of flavors that made people want to try or continue smoking it, and also gave both smokers and non-smokers the impression that shisha is safe, or safer than cigarettes. In addition, shisha smoking was also driven by curiosity about other product attributes such as the smoke; beliefs that it was helpful for coping with challenging life situations such as stress, sadness or joblessness; limited knowledge on the negative health effects; the availability of and ability to smoke shisha in many places, including places where cigarette smoking is prohibited; and poor enforcement and compliance monitoring of the existing tobacco control laws. The presence of friends and family members who smoke shisha, coupled with the need to belong during social events, also played a significant role in promoting shisha smoking.
On the other hand, negative societal views towards shisha smoking and the high costs of shisha discouraged people from smoking it. Additionally, the research indicates that quitting shisha smoking without support is a challenging endeavor.
Implications for public health
This study makes a significant contribution to evidence for decision-making in regards to public health. Restrictions on flavors, strengthening compliance monitoring and enforcement of the tobacco control laws in relation to shisha (e.g., smoke-free environments in indoor and outdoor public places; having health warnings in English on shisha products; and tax measures) have the potential to minimize initiation and use, and to protect the health and wellbeing of Nigeria’s general public.
Dr. Mdege states, “We conducted this study as a response to an expressed need from the tobacco control community in Nigeria for data to inform policy-decisions on how to tackle the alarming surge in shisha smoking. We, therefore, hope that this research and the underlying data will contribute to strengthening tobacco control efforts in Nigeria as well as in other similar contexts.”
The full research paper is available here at PLOS Global Public Health. Access our tobacco control data for Nigeria here.
Share
Recent Posts

Shared Struggles, Shared Solutions: Education and Cross-Sector Data Use Insights
This blog draws on DG’s experience in climate, health, aid management, and agriculture to explore connections between the challenges of data collection, data hosting, and data governance across different sectors and what the solutions to overcoming them can teach us about strengthening education data systems.

Economic Toll of Tobacco-Related Diseases in Kenya: New Research Findings
Development Gateway: An IREX Venture (DG) is pleased to announce the publication of a research manuscript on the Economic Costs of Tobacco-Related Illnesses in Kenya. This research was carried out as part of the Tobacco Control Data Initiative (TCDI) activities in Kenya and is part of a broader report on Morbidity and Mortality from Tobacco Use in Kenya.

The Data Crisis Following USAID’s Withdrawal: Opportunities to Reimagine Data Systems
For decades, USAID and other US government funding supported global data systems, from health surveys and early warning tools to digital infrastructure for ministries. The abrupt termination of USAID funding has triggered twin crises: a halt to data collection and the undermining of digital systems – reveal existing inefficiencies and instabilities in how data is collected, managed, and shared both within and between countries.